Evaluation of Coronary Artery and Aortic Valve Calcium Score Using Low Radiation Dose Non-Gated Chest Computed Tomography
pp.328-331
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.7775/rac.es.v89.i4.20415Keywords:
Tomography, X-Ray Computed - Prevention - ImagingAbstract
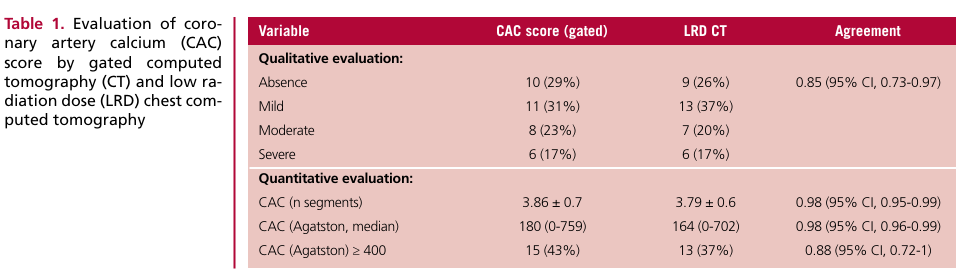
Background: Coronary artery calcium (CAC) score is a prevention tool scarcely used, in part due to its high cost which should not be higher than that of chest computed tomography (CT). Conventional chest CT scan has a predictive value similar to that of gated CT to evaluate CAC using visual or semi-quantitative scales.
Methods: In this retrospective and observational study we included patients (n = 35) undergoing low dose radiation non-gated chest CT and gated CT with evaluation of CAC score within the same hospital stay.
Results: We identified good agreement between the methods for both the qualitative and quantitative assessment, with a mean of 3.86 ± 0.7 segments with coronary artery calcifications identified by gated chest CT, and 3.79 ± 0.6 segments using low radiation dose non-gated chest CT (concordance correlation coefficient 0.98 [95% CI 0.95-0.99]); CAC score assessed by Agatston units was underestimated by 9.8%.
Conclusion: In this study, we demonstrated that low radiation dose CT could accurately provide qualitative and quantitative assess
ment of CAC score.
How to cite this article:
Rodríguez Granillo G. Evaluation of Coronary Artery and Aortic Valve Calcium Score Using Low
Radiation Dose Non-Gated Chest Computed Tomography. REV ARGENT CARDIOL 2021;89:328-331.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2021 Argentine Journal of Cardiology

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.













